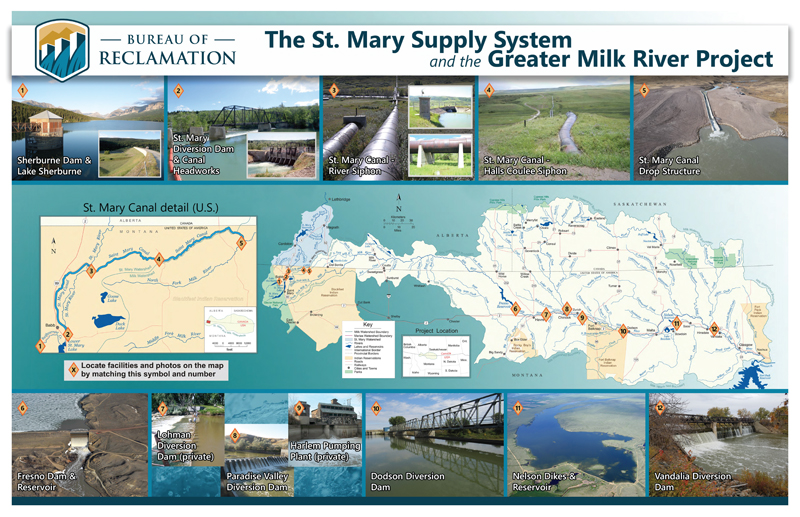
The Milk River Project is a remarkable engineering achievement with a rich history and significant importance to the region it serves. Here are some key points about this project:
Historical Significance: The Milk River Project has a history that spans over a century. It represents a major engineering feat and a testament to the vision and determination of the individuals and organizations involved in its development.
Water Diversion: The project diverts water from the St. Mary River, which flows through northern Montana and Glacier National Park, and extends into southern Alberta, Canada. This diversion is critical for meeting the water needs of various stakeholders in the region.
Water Delivery System: The project utilizes a complex network of canals, siphons, and diversions to distribute water to its intended beneficiaries. This system ensures a continuous and reliable supply of water for agricultural, municipal, and industrial purposes.
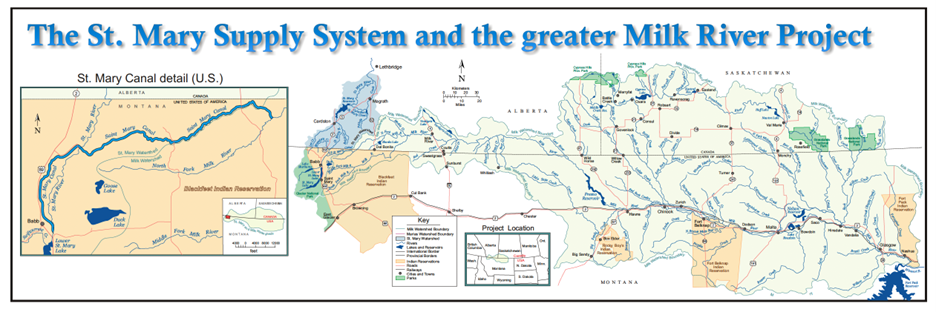
Beneficiaries: The Milk River Project serves a wide range of users, including eight irrigation districts, Reclamation pump contracts, private contracts, and Native American reservations such as the Blackfeet and Fort Belknap Indian Reservation. These users depend on the project to support their water needs.
Recreational Opportunities: The project also has a positive impact on the environment and local communities by providing recreational opportunities. The water supplied by the project contributes to a healthy ecosystem and creates wildlife habitats, enhancing the quality of life for residents and visitors.
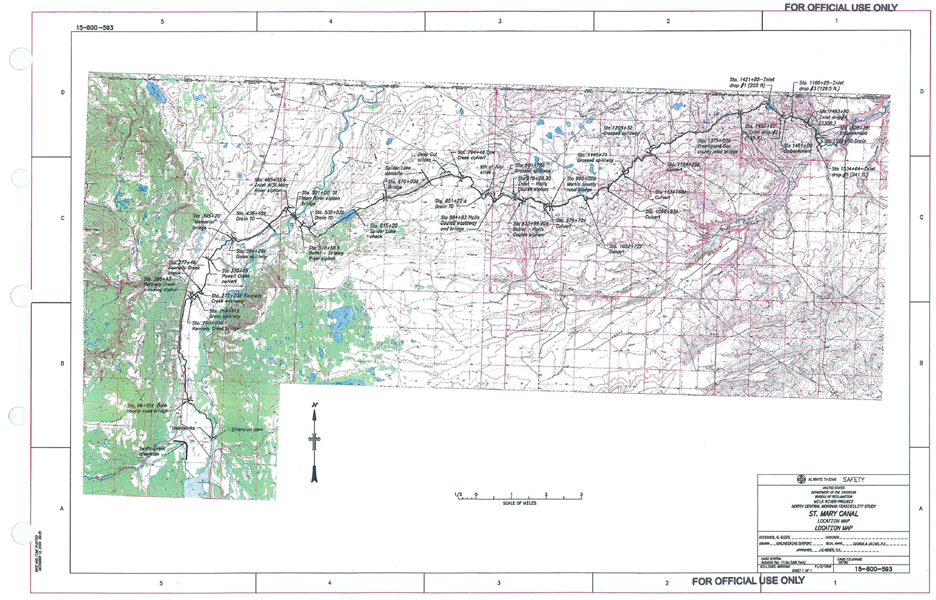
Economic and Social Impact: The reliable water supply from the Milk River Project has significant economic and social benefits for the region. It supports agriculture, which is a crucial industry in Montana, and ensures the availability of water for various other purposes, including drinking water and industrial uses.
“Lifeline of the Hi-Line”: The project’s nickname as the “Lifeline of the Hi-Line” reflects its central role in sustaining life and livelihoods in the region. It highlights the project’s significance and the vital role it plays in the local community and economy.
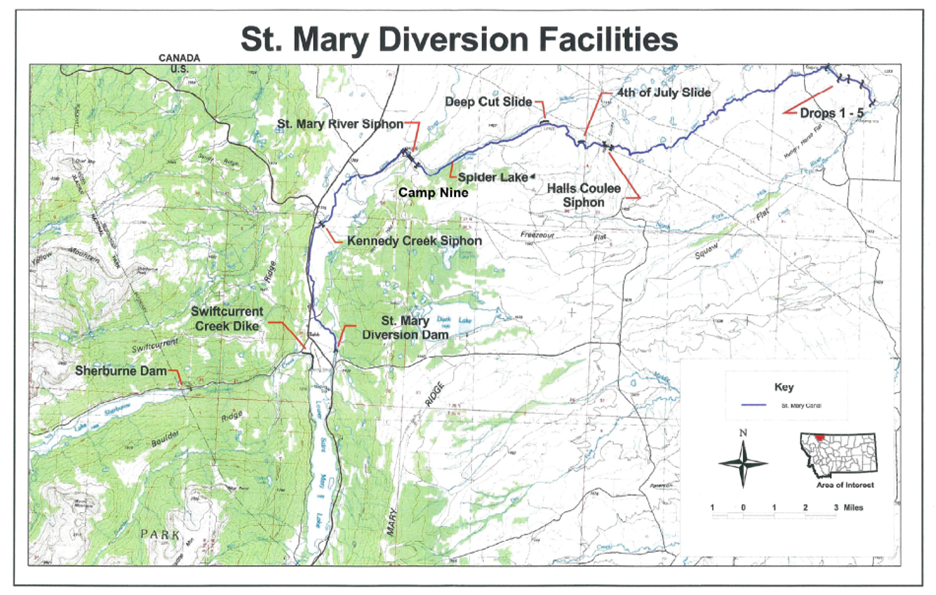
The Milk River Project continues to be a valuable asset for the region it serves, ensuring the sustainable use of water resources and contributing to the overall well-being of the area’s residents and ecosystems.
Failure of Drop Structure 5
The catastrophic failure of Drop Structure 5 (Drop 5) on or about May 16, 2020, had significant and far-reaching consequences for the St. Mary Facilities and the surrounding region. The failure of this structure had several critical impacts:
Water Supply Disruption: The failure of Drop 5 resulted in the inability to deliver water from the St. Mary Facilities. This, in turn, posed a severe threat to the reliable supply of water for irrigation, which is a fundamental component of Montana’s agricultural economy. The loss of water delivery capacity would effectively eliminate approximately 10% of Montana’s irrigated agricultural production.
Economic Impact: The disruption in water supply had the potential to devastate Hi-Line communities and was likely to have economic repercussions across the state of Montana. Agriculture is a crucial sector of the state’s economy, and any reduction in irrigation water availability can have a cascading effect on crop production, farm income, and related industries.
Environmental Damage: The failure of the canal, siphons, or drop structures posed a threat of substantial environmental damage, particularly on the Blackfeet Reservation in southern Alberta. This likely refers to potential ecological harm and habitat disturbance in the event of uncontrolled water releases.
Water Rights Compacts Jeopardized: The system’s failure also had implications for the Fort Belknap and Blackfeet Federal Reserved Water Rights Compacts. Water rights compacts are legal agreements that determine the allocation and use of water resources, and the failure of the infrastructure could jeopardize the fulfillment of these compacts, leading to legal and regulatory complications.
The failure of Drop 5 had a broad range of consequences, affecting not only the local agricultural sector and communities but also extending to environmental and legal concerns. The incident underscores the critical importance of maintaining and modernizing water infrastructure to ensure the reliability of water supply for both economic and environmental sustainability.
For more information on the Drop 5 Failure, visit:
St. Mary Drop 2 & 5 Emergency Repairs – Milk River Irrigation (milkriverproject.com)
Interactive Project Map:
https://www.milkriverproject.com/about/interactive-project-map/
Project Story Map:
https://www.milkriverproject.com/about/story-map/
For an historical timeline of the Milk River Project, visit:
https://www.milkriverproject.com/about/milk-river-basin-and-history/#